Fed raises interest rates often leads to an increase in the cost of capital in international financial markets. This can affect businesses and banks in Vietnam as they face increased borrowing costs, affecting their ability to invest and expand.
1. What is the FED interest rate hike?
The US Federal Reserve (FED) interest rate is an important factor for those interested in the international investment market. As a key indicator, the FED rate strongly affects global investment behavior. Interest rates are the cost of capital, and their increase or decrease can change the cost of borrowing and the return on investment. When the FED raises interest rates, the cost of borrowing increases, reducing the attractiveness of risky investments and affecting the value of assets. Conversely, lowering interest rates can stimulate investment and increase asset values.
About the FED
The Federal Reserve (FED) was modeled after the New York Clearinghouse, which existed in New York during the 19th and 20th centuries. The US Central Banking System (also known as the Federal Reserve, or FED) is the most powerful economic institution in the United States and the world. Its core responsibilities include setting interest rates, managing the money supply, and regulating financial markets.
The Fed also acts as a lender of last resort during times of economic crisis. As the US economy recovers, rising inflation has drawn the attention of the central bank. The Fed is also one of the most politically independent institutions of the US government, and has long been at odds with lawmakers and presidents, including the occupant of the White House.
The FED is considered the most powerful financial institution in the world, this is the only place that prints USD. The key currency in international trade today is the USD. Most import and export activities use USD as the standard unit of payment. Important items such as oil and gold are priced in USD. The only agency with the authority to intervene in determining the value of the USD through foreign exchange activities or buying and selling USD is the FED.

What is the FED interest rate?
Federal Funds Rate is the English name of the term Federal Funds Rate. It is understood as the interest rate at which banks lend to each other for a period of one day (or overnight loans) to obtain an amount equal to the FED's required reserve requirement.
Fed interest rate is a tool that the FED uses to control the growth of the US economy and is the benchmark for interest rates on credit cards, mortgages, bank loans and many other things. The FED's interest rate policies not only affect the US economy but also many other countries around the world. This interest rate will be the foundation and when the FED raises interest rates, it causes significant fluctuations in the financial markets, especially the US dollar.
Most import and export activities use USD as the standard unit of payment. In particular, the only place that can decide the increase or decrease of USD interest rates is the FED. From there, this directly affects the strength of the USD and creates some effects on US trading partners. Important commodities such as oil and gold are priced in USD, proving the important position of this unit in the world monetary system. The only agency with the authority to intervene in determining the value of the USD through foreign exchange activities or buying and selling USD is the FED. This also means that the FED's control of USD also indirectly controls the global market. So the FED's decisions affect the global economy.
The Fed's ups and downs
Fed interest rate increase: Interest rates such as loan interest rates, deposit interest rates or bond interest rates must be based on the FED interest rate. When this interest rate increases, other interest rates on the market must also increase. When interest rates increase, it will limit the lending needs of individuals or organizations operating in the market economy.
Fed interest rates fall: On the contrary, when borrowers borrow a lot, the FED interest rate will also decrease. This will stimulate the increase in demand of investors, thereby stimulating the global economy. When the economy is in a stable state but still maintains low interest rates, the use of capital is ineffective, thereby creating high risks in the market. Asset bubbles and high inflation rates are the two most common phenomena when the FED has low interest rates. At this time, the market is in danger of sustainability as well as causing economic crisis.
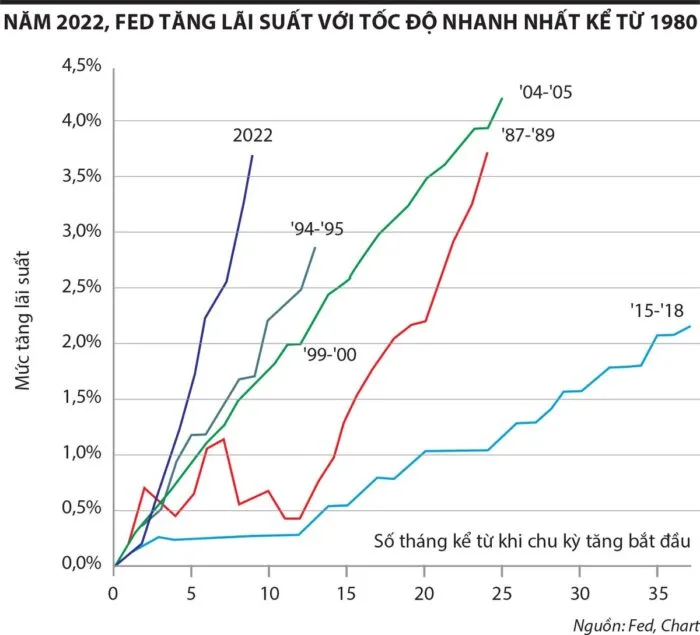
In 2022, the FED raised interest rates at the fastest rate since 1980.
Function of Fed interest rate
Plays a key role for US central banks: The federal funds rate is one of the most important indicators for the US economy, having a huge impact on many aspects of financial and currency markets. It is not only an important indicator but also plays a key role in the policies of the US central bank.
Providing financial services, operating the national payment system: The US central bank, or FED, makes policy decisions that directly affect the US economy and the value of the USD. Every move of the FED is not only of concern to the US economy but also to the whole world. The FED's policy aims to maintain stability in the economy and limit systemic risks in the financial market. The federal funds rate also affects short-term interest rates, as lenders often set their interest rates based on the prime rate. Changes in the federal funds rate can cause fluctuations in short-term interest rates, affecting the cost of borrowing and lending in the financial system.
Supervision and regulation of organizations and banks: US Federal Funds Rate also plays an important role in supervising and regulating banking institutions. Changes in these rates often cause strong reactions in the stock market. Investors closely monitor the federal funds rate, and even a small change can affect the behavior of financial markets. Analysts in the securities investment industry pay special attention to the members of the FOMC to predict the direction of the target interest rate.
2. Why did the FED raise interest rates?
The FED can adjust interest rates based on inflation rates to maintain economic stability. When inflation rates rise, Fed raises interest rates to reduce the amount of money lent by banks. This has the simultaneous effect of reducing people's demand for loans and consumption. Increasing interest rates also makes consumer debt more expensive, encouraging people to reduce spending, thereby reducing demand and putting downward pressure on prices of goods and services.
Conversely, when inflation falls, it means that people may reduce their spending. This is a sign of economic recession. In this situation, the FED often considers lowering interest rates to stimulate economic recovery. Low interest rates help make loans cheaper for businesses and consumers, promoting economic growth.
In March 2023, the Fed decided to raise interest rates, a decision that came after US inflation surged to a 41-year high of 9%. Interest rates rose to their highest level since 2007, but inflation remained at about twice the Fed's target of 2%.
The Fed's forecast shows that the core inflation rate and headline inflation rate by the end of 2023 are 3.9% and 3.2%, respectively. The interest rate hike is aimed at controlling inflation and maintaining economic stability, especially after the difficult period of the Covid-19 pandemic. In 2021, global GDP growth recovered from -3.1% in 2020 to 6% in 2021. However, the Russia-Ukraine conflict disrupted gas supplies, causing energy prices to skyrocket, increasing global inflationary pressure to 7.9% in the second quarter of 2022.
Faced with the challenge of inflation and global economic pressures, Fed raises interest rates is an important measure to maintain stability and control the financial situation. High interest rates have negatively affected many countries, including Vietnam, and may create new challenges for the global economic recovery.
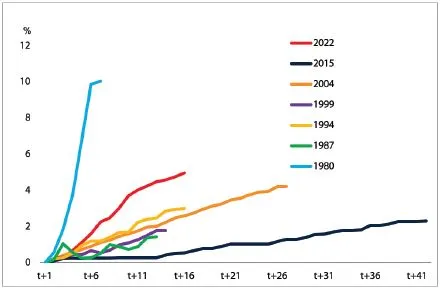
FED Rate Hikes – Source: World Banka, 2023
3. How does the Fed's interest rate hike affect the global economy?
The FED's impact on the global economy in the short term will have a negative impact on the economic recovery (due to reduced consumption and investment), possibly pushing the US economy into recession, although the FED currently believes that the US economy is still stable.
Some experts also believe that the fluctuation of US government bond interest rates when the yields of 2, 3 and 5 years tend to converge (long-term interest rates equal short and medium-term interest rates). This is also a sign that the US economy is at risk of falling into recession in the near future.
However, the Fed is currently communicating a moderate message that the 75-point increase is an unusual and timely increase. The Fed believes that similar moves may not be made many times in the future, demonstrating that the Fed is concerned about the risk of stagflation (the economy stagnates when inflation is high) in the economy.
Second, US interest rates are forecast to rise to 3.41 TP3T by the end of 2022 and to 3.81 TP3T in 2023. This will increase the cost of capital and debt servicing costs of households and businesses, while slowing the US economy. However, the increase will be more stable when inflation is gradually controlled and unemployment returns to the pre-COVID-19 level of 3.51 TP3T.
In addition, the Russia-Ukraine tension still exists; China's Zero Covid policy, along with the disruption and breakage of the global production and supply chain, makes it difficult for the price level to decrease, so the FED must continue to narrow its monetary policy.
Third, the FED's interest rate increase causes the USD exchange rate to increase against other domestic currencies, creating favorable conditions for exports. However, this makes imports difficult and creates pressure on imported inflation for countries with increasing trade deficits.
Fourth, rising interest rates cause financial market volatility, including a shift in indirect investment capital. Accordingly, some investors will seek refuge in safer channels. They tend to shift part of their investment portfolio back to the US and other regions, where interest rates are higher and risks are acceptable.
4. How does the Fed's interest rate hike affect Vietnam?
The Fed’s tightening monetary policy, stemming from its efforts to curb inflation, is posing challenges to the recovery of developing economies, including Vietnam. In this context, implementing an expansionary monetary policy in Vietnam may only have limited effectiveness, and the economy will face greater trade-offs between inflation, exchange rates and growth.
Given the current state of the Vietnamese economy, expansionary monetary policy can create a mitigating effect, while the room for implementing fiscal policy is still large and needs to be utilized more effectively in the coming period. This poses an important challenge, requiring flexibility and innovation in economic management to cope with global fluctuations and maintain stability in the Vietnamese economy.
Vietnam, an open economy with a small scale compared to the world economy, has a large trade openness but low financial openness. The FED's decision to raise interest rates in 2022 and the first half of 2023, stemming from price shocks, has a more negative impact on developing countries and Vietnam in particular. In this context, measures to promote growth through monetary policy may have limited effectiveness, due to the weak absorption capacity of the corporate sector, leading to a greater trade-off between inflation, exchange rates and growth.
Early morning of September 22 (Vietnam time), the FED decided to raise interest rates by 75 basis points after a 2-day meeting. Thus, the FED decided to raise interest rates to 3 - 3.25%. The head of the US Federal Reserve also mentioned the possibility that this agency will continue to raise interest rates to curb inflation. For the Vietnamese economy, the decision of the US Federal Reserve (FED) to raise interest rates will create significant impacts, although to a lesser extent than other emerging and developed countries.
The FED's tight monetary policy affects Vietnam's economy and stock market.
First, Vietnam’s trade activities may slow down as the global recovery falters. The Fed’s interest rate hikes form a trend of central banks around the world to control inflation, increasing borrowing costs for businesses and consumers in Vietnam, posing challenges in investment and consumption decisions.
Second, the USD increased in value due to the sharp increase in FED interest rates, creating greater pressure on the USD/VND currency pair. The USD/VND exchange rate increased by more than 1.65%, and the DXY index increased to 9.9%, negatively affecting our country's exports and economy.
Third, domestic interest rates are expected to rise slightly, putting pressure on new borrowing costs and debt service obligations in USD. At the same time, funding sources in the international market may become more difficult, posing a major challenge to the Vietnamese economy and businesses.
Finally, the impact on Vietnam stock market is inevitable. The tightening global financial situation and pressure from rising interest rates may dampen the growth prospects of the Vietnamese stock market, especially in the context of tight monetary policy. The plan to reduce the amount of bonds purchased by the FED. The Vietnamese stock market has experienced a sharp decline in recent months. Investors need to be cautious and flexible to adapt to fluctuations in the international financial environment.
Conclusion: Vietnam is ready to cope with economic pressure from rising interest rates
The Fed's interest rate hike that began in early 2022 and has lasted until now is the fastest and strongest interest rate hike in the past 40 years. This interest rate hike is the Fed's response to high US inflation due to rapidly rising world energy prices. High USD interest rates combined with the world economy in general and the US economy in particular slow recovery after the Covid-19 pandemic are major challenges for emerging economies, including Vietnam.
In that context, there is not much room for implementing monetary policy due to the weak absorption capacity of the economy for credit, as well as the pressure of the VND-USD interest rate gap which will negatively impact the exchange rate. There is still a lot of room for fiscal policy due to low public debt and the huge demand for public investment in energy and sustainable growth in Vietnam. This needs to be the focus of policy in the coming period.
Source: Onstocks